Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal Nerve
What’s unique about the Glossopharyngeal Nerve?
The glossopharyngeal nerve parallels both the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve along its path. Aspects of its name — “Glosso,” meaning tongue, and “pharyngeal,” meaning pharynx — help imply that the nerve supplies sensory, motor, and parasympathetic functions in the tongue, neck, and throat area.
What is the function of the nerve?
Motor: Innervation of the stylopharyngeus muscle contributing to swallowing and speech
Sensory: Sensation to the oropharynx, middle ear cavity, auditory tube, carotid body and sinus, and the posterior 1/3 of the tongue; taste sensation in the posterior 1/3 of the tongue; also monitors blood pressure and oxygen levels to the brain
Parasympathetic: Innervation of the parotid gland, controlling saliva production
What are the signs of dysfunction?
Signs of damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve may include:
• Difficulty swallowing
• Impairment of taste over the posterior one-third of the tongue and palate
• Impaired sensation over the posterior one-third of the tongue, palate, and pharynx
• An absent gag reflex
• Dysfunction of the parotid gland
• Pain in the nose, throat, tongue, ear, throat, tonsils, or voice box
How might this nerve be impacted?
The nerve may be impacted as a result of:
• Trauma to the head or neck
• Tumors
• Arteries or blood vessels compressing the nerve
• Cancer
• Infections
• Complications from medical procedures
• Stroke
• Diseases that affect nerve function
How can you work with this nerve?
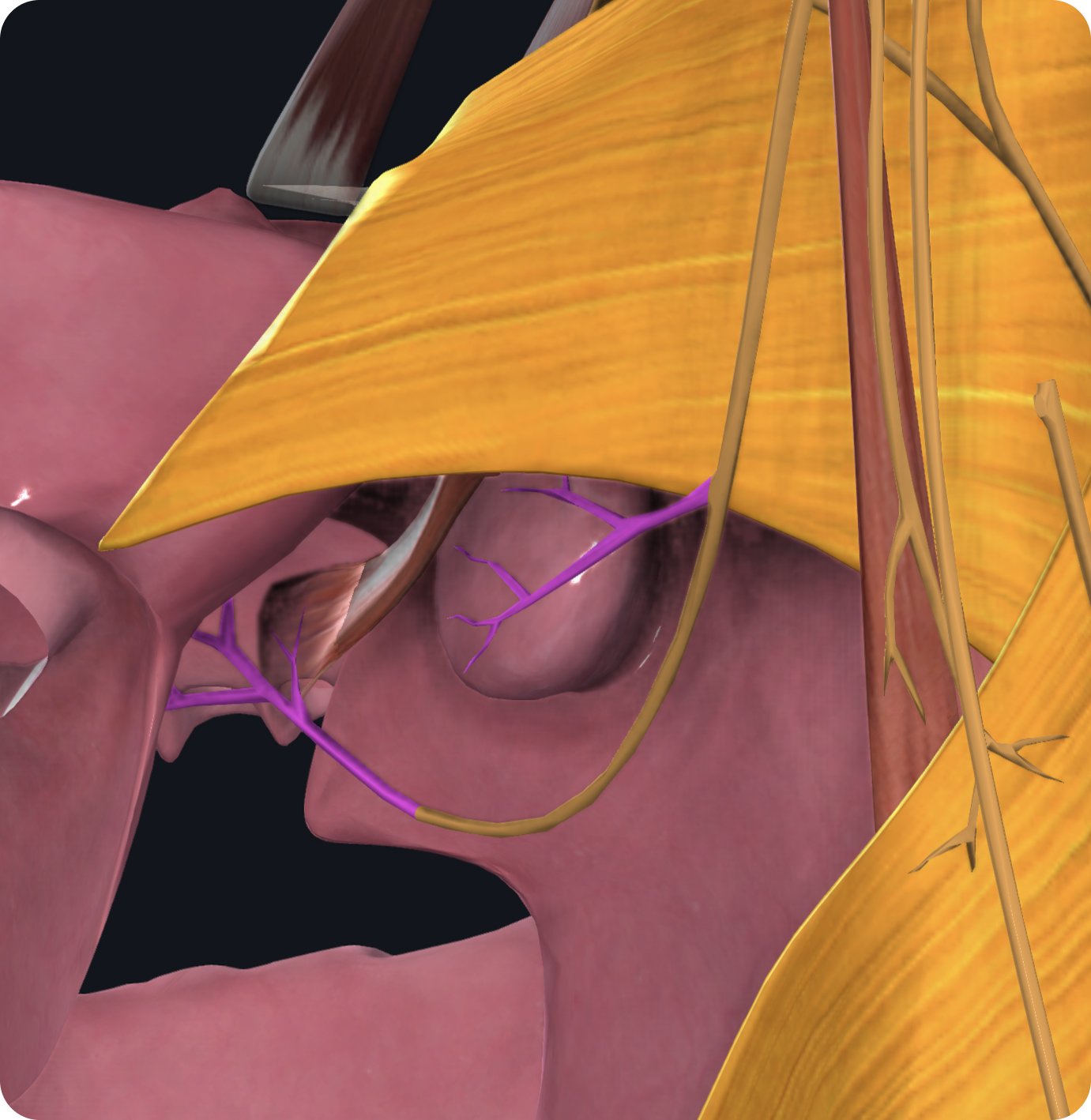
• Notice the brainstem, temporal and occipital bones, internal carotid artery, and jugular veins within the thoracic and cervical regions. Notice if there is a request for decompression in any place, and offer that if so.
• Visualize the pathway, from the medulla, moving laterally alongside cranial nerves X and XI to exit through jugular foramen, and branching out to meet its various targets in the throat and mouth.
• Notice the quality of potency moving through the nerve.
• Hold space for any held patterns along the pathway to shift.
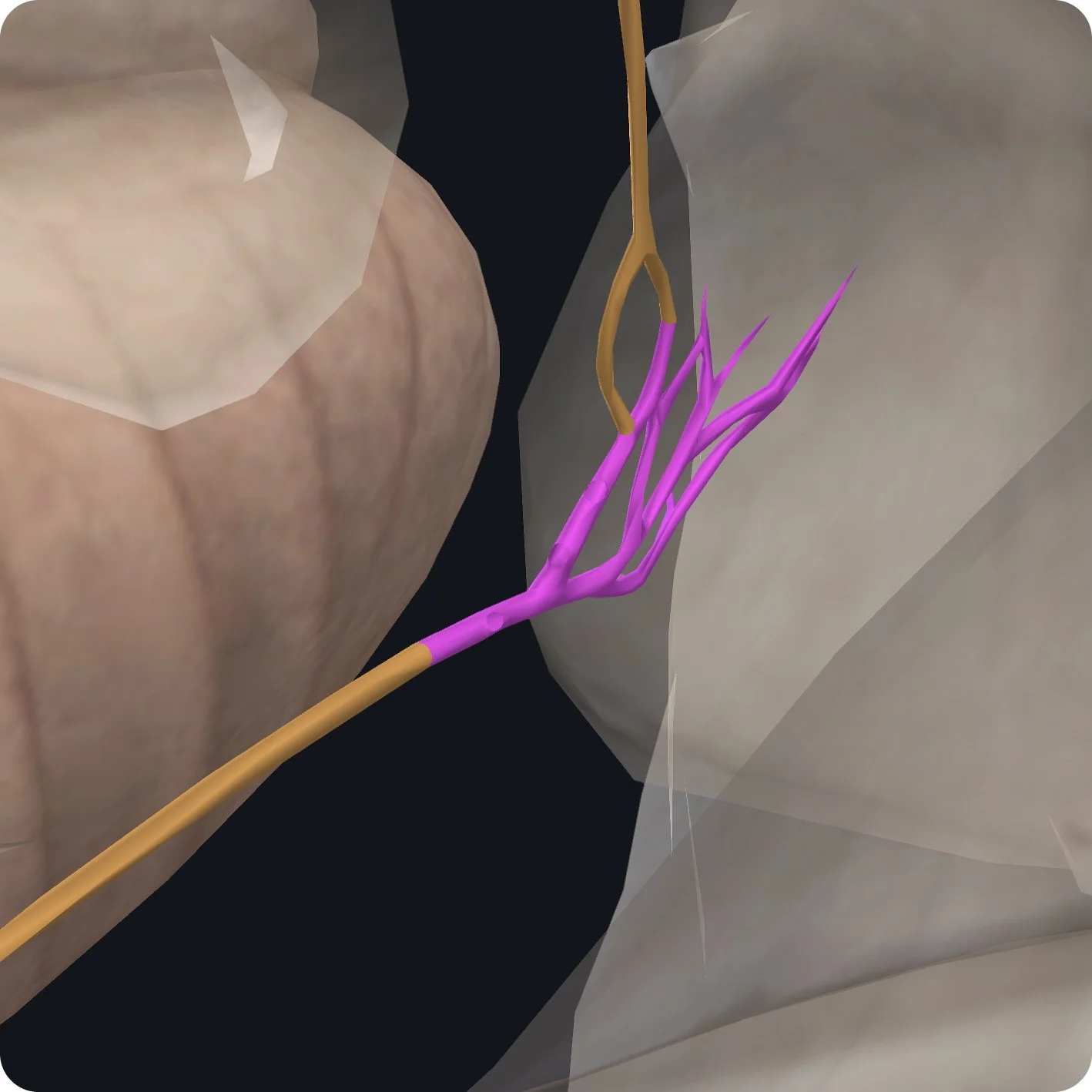
The glossopharyngeal nerve emerges from the medulla on the posterior lateral border of the medullary olive.
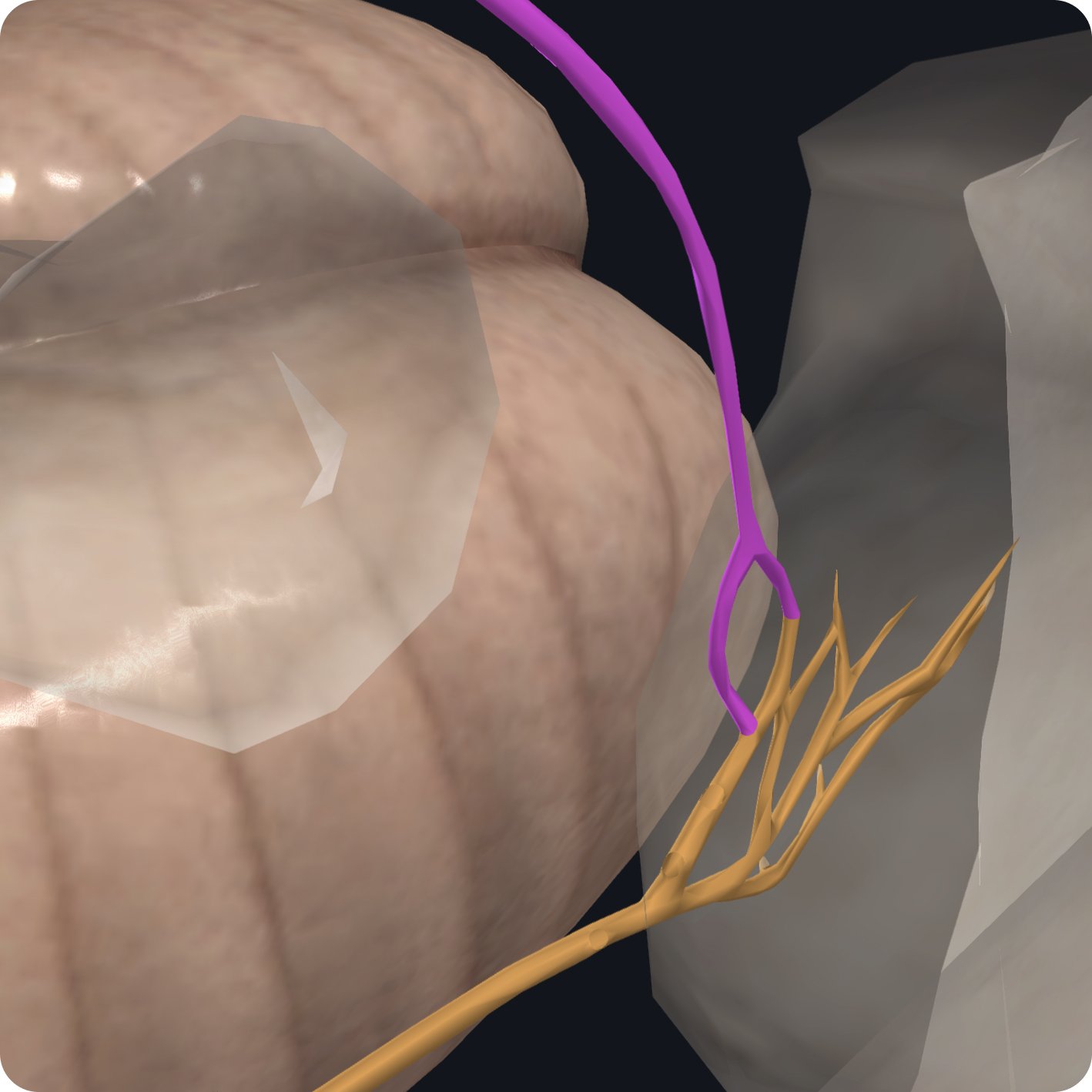
From here, it has a short intracranial journey over the lateral part of the occipital bone to the jugular foramen which is located between the temporal bone and the occipital bone.
The glossopharyngeal nerve has two ganglia the superior ganglion found within the jugular foramen followed by the inferior ganglion found below the exit of the jugular foramen.
The first of six branches arises from the inferior ganglion; it is called the tympanic nerve and it carries general visceral sensory fibers from the tympanic cavity, an auditory tube.
It also carries pre-ganglionic part sympathetic nerve fibers to the tympanic plexus.
The fibers from this plexus form the lesser petrosal nerve.
The lesser petrosal nerve carries secretary motor fibers to the parotid gland.
The remainder of the glossopharyngeal nerve runs inferior and anteriorly passing between the internal jugular vein and internal carotid artery.
Here, it gives off the second branch the carotid sinus nerve.
The carotid sinus nerve supplies the carotid sinus and carotid body.
The third branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve is the pharyngeal branch, which carries general visceral sensory fibers from the oropharynx and surrounding mucosal membranes.
It then unites with the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk to form the pharyngeal plexus supplying the muscles of the pharynx and the soft palate.
The glossopharyngeal nerve gives off a fourth branch the stylopharyngeal branch which wraps around the stylopharyngeus muscle providing motor innervation to this muscle.
The glossopharyngeal nerve then passes into the space between the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles where it gives off two more small branches.
The tonsillar branch carries sensory nerve fibers from the palatine tonsils.
The lingual branch carries special sensory taste fibers from the posterior third of the tongue and provides sensation to this area.